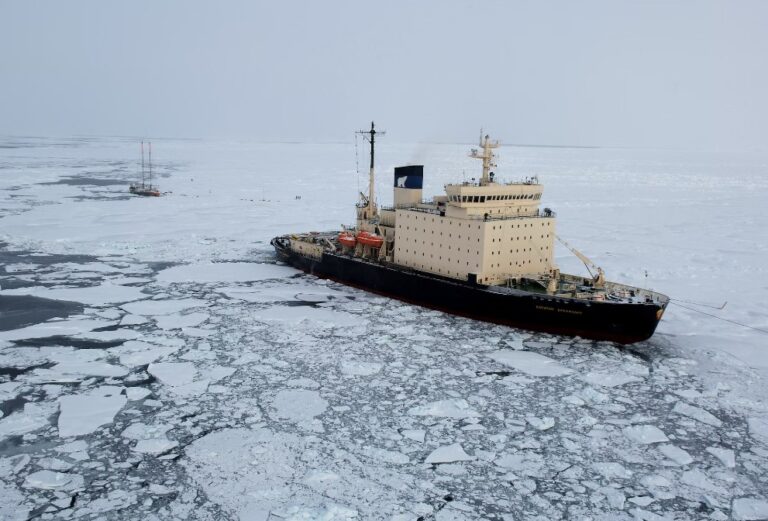
Russia’s state gas company Gazprom delivered the first cargo of liquefied gas (LNG) to China via the so-called “Northern Sea Route,” a shipping route passing through the Arctic. The cargo had left a month ago.
Table of Contents
Why Russia is targeting the Northern Sea Route
Russia believes that the Northern Sea Route – which runs from Murmansk, near the Norwegian border, to the Bering Strait near U.S. Alaska – could become an alternative to the Suez Canal.
Although navigating the route is difficult due to icy waters, the Arctic route would allow Moscow not only to reduce shipping time to Asia, but also to emancipate itself from “bottlenecks” and ports under the control of Western powers, given the deterioration of relations with Europe and the United States following the invasion of Ukraine.
Data, reported by Reuters, say the LNG carrier Velikiy Novgorod was loaded with LNG at the Portovaya facility on the Baltic Sea on Aug. 14. It is now at the Caofeidian terminal in China’s northeastern Hebei province.
Advantages and disadvantages of arctic shipping
Given the sharp decline in sales of natural gas and oil to Europe, historically its main market, Russia is trying to redirect hydrocarbon exports to Asia, and specifically to China.
The Northern Sea Route effectively guarantees the shortest route – about 5300 kilometers – between Europe and East Asia: a Russian ship bound for China passing through the Suez Canal would take twice as long.
Sailing conditions in the Arctic, however, between icebergs and extremely low temperatures, are extremely difficult.
It is unclear whether Russia will be able to overcome these logistical difficulties and make the Northern Sea Route a convenient route for oil and LNG exports to China and the rest of Asia. It lacks tankers, for one thing: those equipped as icebreakers – and thus capable of making such a journey – number just eight, Bloomberg wrote.
Trade passing through the Arctic, therefore, could reach significant volumes only in summer, when weather conditions are better, as in the case of the Velikiy Novgorod.
Read also: The impact and importance of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in today’s energy scene