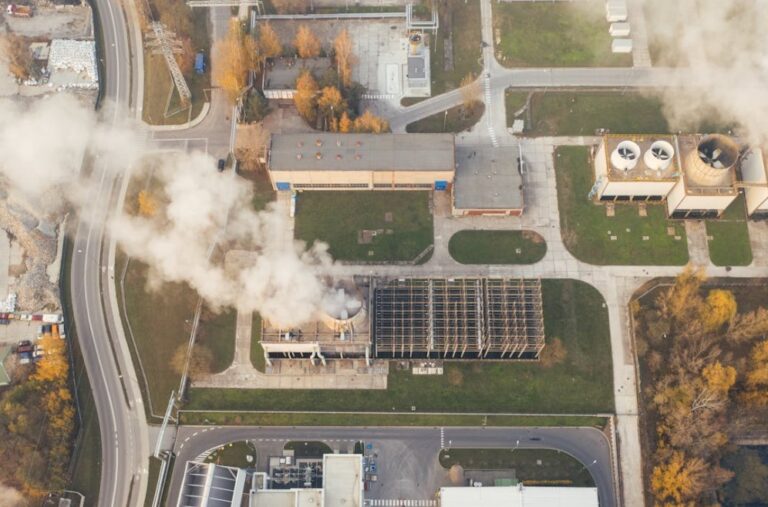
Industrial ecology is a rather recent discipline whose ultimate goal is to reduce industrial pollution, while optimizing company returns and resource management. It is therefore a multidisciplinary science that looks at the environment, as well as the economics of production realities.
Table of Contents
Industrial ecology: what it is
At the basis of this type of ecology is the awareness of the fact that the behaviors of each person, as an individual or as part of a whole, are fundamental in a green economy context and with a view to a greener and more eco-friendly vision.
Scientist Robert Frosch thus defined industrial ecology: the set of practices intended to reduce industrial pollution.
In practice, it is therefore a discipline that aims to reduce the impacts of industrial production on the surrounding environment, in order to protect its balance and enhance its resources.
What is meant by industrial ecology
Also referred to as the ‘science of sustainability’, industrial ecology is a science whose aim is to redefine industrial activities to make them more sustainable. In other words, it concerns the responsible behavior of companies.
In practice, it evaluates and analyzes company flows, both in terms of energy and materials, in order to study how to reduce their impacts on the environment. It has an interdisciplinary approach that involves ecology, economics, engineering, business management, as well as legislative bodies and public administrations.
At a global level, the new industrial ecology is defined as a circular economy and concerns every sector: industry, agriculture, fashion, finance, mobility, waste management and many others.
This discipline imposes a radical change in the modus operandi of companies for everything that concerns the efficient use of natural resources, through the application of principles such as eco-design, the use of renewable energies, the recovery of materials, the modularity and versatility.
What industrial ecology deals with
It is a rather complex discipline that involves multiple areas of study.
Basically, in fact, it studies the impacts that industrial activities have on ecosystems and the availability of natural resources. But it’s not limited to that. In fact, industrial ecology, in addition to the mere environmental problem, looks at the industrial system as a whole.
Therefore, in addition to addressing issues relating to the environment and pollution, it also considers other aspects of the industrial process, such as technologies, the interrelationship of companies, the economics of processes, in order to be able to plan a profitable economic model for corporate realities, at the same time optimize the use of already scarce resources.
With this logic, we can also talk about green economy applied to industry, and it appears to be particularly relevant in developing countries.
What are the objectives of industrial ecology
As already repeated, industrial ecology is a multidisciplinary science that studies and analyzes the interaction between industrial activity and the environment in order to minimize the impact of production processes.
The primary aim of this science is therefore to design and create products in such a way as to be able to manage and limitate the production of waste and emissions.
In other words, the goal is to make all human activities more sustainable. Obviously, to be able to achieve this objective, we must first move from a linear economy system to a system based on the circular economy.
Giving practical examples, it is necessary to:
- reduce polluting emissions;
- optimize the use of energy and materials;
- apply the technologies of recycling and recovery of materials;
- extend the responsibility of producers in all phases of product development: design, production, distribution and end-of-life management;
- internally manage the costs for disposing of production waste.
Advantages
Specifically, thanks to the application of the principles of this discipline there would be numerous advantages, such as:
- reducing the impacts of companies on the environment;
- less waste of resources;
- greater incentives for companies to identify new technologies useful for making their business less impactful;
- strengthen the company brand, acquiring greater credibility and reliability;
- conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity;
- lower energy and material consumption, which translates into lower costs for the company itself.
Disadvantages
There can be no question of real disadvantages. However, various limitations contribute to the practical application of the discipline. In fact, the tools listed above are often difficult to create due to various reasons, such as:
- poor ability of companies to evaluate the beneficial effects of ecological investments;
- lack of knowledge on the part of companies of the possibility of being able to proceed with sustainable activities;
- lack of sufficiently strong political support to incentivize green investments.
Read also: Bioeconomy: what is it and why it will help to eliminate fossil fuels