Today’s world economy presents a complex web of national debt burden, with many countries struggling with high liabilities. In this fiscal challenge, a select group of nations stands out for maintaining minimal debt burdens. This article sheds light on countries that have successfully kept their national debt low compared to their Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
These countries’ low national debt levels result from robust fiscal discipline, sustained economic growth, and cautious policy-making. They are often praised for their financial prudence and serve as benchmarks for other nations striving to curb their debt.
Table of Contents
Top 5 countries with the least national debt burden
The following are the 5 countries with the least national debt burden:
1. Brunei
Brunei showcases exceptional economic stability within Southeast Asia, maintaining one of the world’s lowest national debt ratios to GDP. The nation’s prosperity, fueled substantially by its oil and gas industry, provides a solid foundation for its impressive fiscal health.
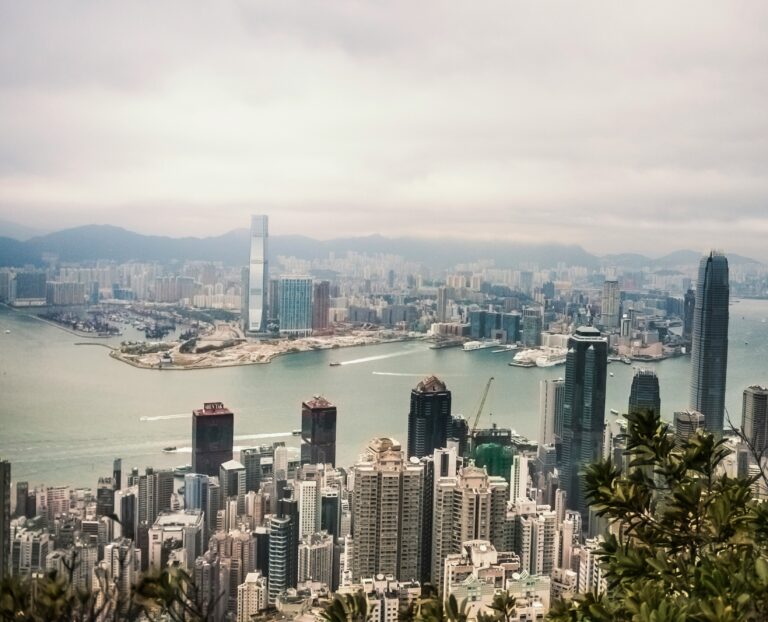
2. Hong Kong
Hong Kong stands out as a global financial center, exhibiting remarkable financial discipline. This discipline, paired with effective monetary policies, ensures that Hong Kong consistently maintains one of the world’s lowest levels of national debt.
3. Estonia
Estonia, a small nation in the Baltics, is recognized for its minimal national debt burden. The country’s success is attributed to a thriving technology sector and the implementation of stringent fiscal policies that uphold a balanced budget, leading to a favorable debt-to-GDP ratio.
4. United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates, enriched by its substantial oil reserves, has a notably low level of national debt. The nation’s economic strategy, marked by diversification and prudent financial management, allows it to sustain a low debt-to-GDP ratio, underscoring its economic resilience.
5. Algeria
Algeria, situated in the heart of North Africa, has achieved commendable low levels of national debt as a result of the country’s prudent economic management. Rich in natural resources, especially hydrocarbons, Algeria leverages these assets to fortify its fiscal position. The combination of these abundant resources and astute policy-making contributes to the nation’s favorable debt-to-GDP ratio, distinguishing Algeria in the region for its financial stewardship.
Factors contributing to low debt burden
The following factor plays a pivotal role in shaping a nation’s financial health and its capacity to operate without excessive borrowing.
Natural resources
Countries rich in natural resources, particularly hydrocarbons and minerals, often enjoy a strengthened economic position. These resources provide a significant revenue source, which can be used to fund government operations, thus reducing the need to borrow. For example, a country with substantial oil reserves can export this commodity to generate income, thereby maintaining lower debt levels.
Read also: The 10 countries with the most valuable natural resources worldwide
Economic growth
The role of economic growth in managing debt cannot be overstated. A growing economy translates into more jobs, increased consumer spending, and higher tax revenues. With an expanding financial base, a government can fund its policies without accumulating debt, which in turn helps preserve a low debt status.
Financial controls
Effective financial controls are fundamental in achieving and maintaining low debt levels. Strong financial institutions and sound regulatory frameworks ensure government spending is responsibly executed. Such oversight helps to prevent excessive borrowing and maintains debt within manageable limits. Moreover, these controls support the government in identifying and eliminating wasteful expenditures, further reducing the need for debt.
Balanced budget policies
Balanced budget policies are pivotal in the quest to maintain low national debt. Governments adhering to such policies strive to equate their spending with revenue, curtailing the need for excess borrowing. This fiscal conservatism lays the groundwork for low national debt levels. Countries dedicated to budget equilibrium generally exhibit a high degree of fiscal discipline, equipping them with the necessary tools to manage their debts efficiently.
Impact of low national debt
The implications of low national debt extend across the economic spectrum, influencing a country’s financial dynamics and its citizens’ quality of life. A low debt burden fosters a stable macroeconomic environment, where governments can invest in public services, infrastructure, and social programs without the high cost of interest payments that accompany high levels of debt.
Financial markets tend to favor countries with low debt, as it suggests fiscal responsibility and a lower risk of default. This confidence translates into better credit ratings, which can reduce borrowing costs and attract investment. A country perceived as a safe investment destination can draw both domestic and foreign investors, leading to job creation and economic diversification.
For citizens, the direct benefits of low national debt are manifold. It can mean lower taxes, as governments don’t need to levy high rates to service debt. It can also result in more significant government spending on healthcare, education, and welfare, contributing to higher living standards and social welfare.
Moreover, low national debt can provide a buffer against economic shocks. Countries with room in their budgets can respond more effectively to crises, whether natural disasters, economic downturns, or unforeseen events, without having to increase debt substantially. This resilience is invaluable for maintaining economic stability and protecting the nation’s long-term financial health.
Read also: The countries with the highest national debt burden globally